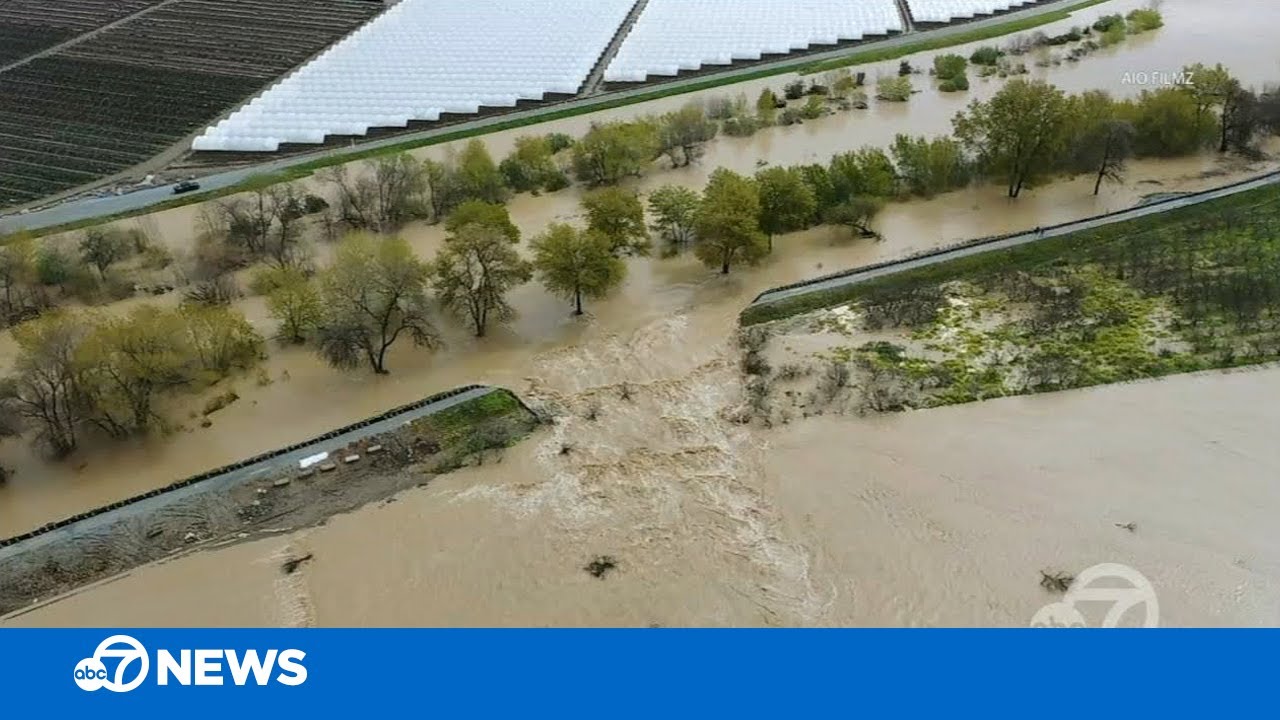
In latest weeks, highly effective atmospheric river storms have swept throughout Washington, Oregon and California, unloading enormous amounts of rain. As rivers surged, they overtopped or breached multiple levees – these lengthy, typically unnoticed boundaries holding floodwaters again from houses and cities.
More often than not, levees don’t demand consideration. They quietly do their job, 12 months after 12 months. However when storms intensify, levees instantly matter in a really private means. They’ll decide whether or not a neighborhood stays dry or finally ends up underwater.
The harm within the West displays a nationwide drawback that has been constructing for many years. Throughout the U.S., levees are getting older whereas weather is getting more extreme. Many of those constructions had been by no means designed for the big duty they now carry.
AP Photo/Manuel Valdes
As a civil engineer at Tufts College, I examine water infrastructure, together with the vulnerability of levees and techniques for making them extra resilient. My analysis additionally reveals that when levees fail, the consequences don’t fall evenly on the inhabitants.
Levees grew to become important infrastructure virtually by chance
Many individuals assume levees had been constructed as a part of fashionable, rigorously engineered flood-control programs. In actuality, lots of the levees nonetheless in use right now started way more humbly.
A long time in the past, farmers built simple earthen embankments to guard their fields and livestock from seasonal flooding. These early levees had been sensible options, formed by expertise slightly than formal engineering. They weren’t constructed utilizing rigorous design requirements, and they didn’t comply with constant building or upkeep pointers.
Over time, the panorama round these levees modified. Farmland gave strategy to neighborhoods. Roads, railways, factories and ports expanded into floodplains. Populations grew. What had been as soon as modest, native constructions defending farms regularly grew to become the primary line of protection for millions of people in houses and workplaces.

National Weather Service Archival Photography by Steve Nicklas, NOS, NGS
With out a lot public debate or planning, these semi-engineered levees took on a important and unintended position. The question that still lingers is whether or not they had been ever ready for it.
Huge, ageing levee system now defending thousands and thousands
At this time, the National Levee Database counts greater than 24,000 miles (38,600 kilometers) of levees within the U.S., with a mean age of about 61 years and plenty of of them a lot older. Collectively, they shield over 23 million individuals, round 7 million buildings and practically US$2 trillion in property worth.
That’s a rare stage of duty for a system that’s inconsistently maintained with various oversight. Some levees are inspected repeatedly. Others are owned by small local agencies or private entities with restricted funding. In some circumstances, duty is unclear or fragmented.
One levee that was breached alongside the Inexperienced River in Washington state throughout storms in mid-December 2025 had been due for repairs for a number of years, however disagreements amongst governments had just lately held up wanted work, The Seattle Times reported. The breach pressured thousands of people to evacuate
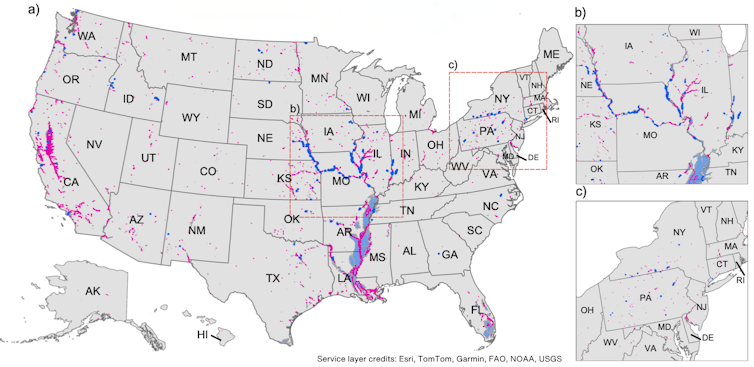
S. Flynn, et al., 2025
The American Society of Civil Engineers’ 2025 Report Card for American Infrastructure, which I contributed to, gave the nation’s levees a D-plus grade, citing ageing infrastructure, inconsistent monitoring and long-term underinvestment. A brand new dataset that colleagues and I created of levee harm contains 487 cases where rivers poured over levees, referred to as overtopping, previously 15 years. That doesn’t imply levees are failing in all places; it implies that many are working with little margin for error.
How levees fail
Levee failures are not often sudden collapses. Extra typically, they begin quietly.
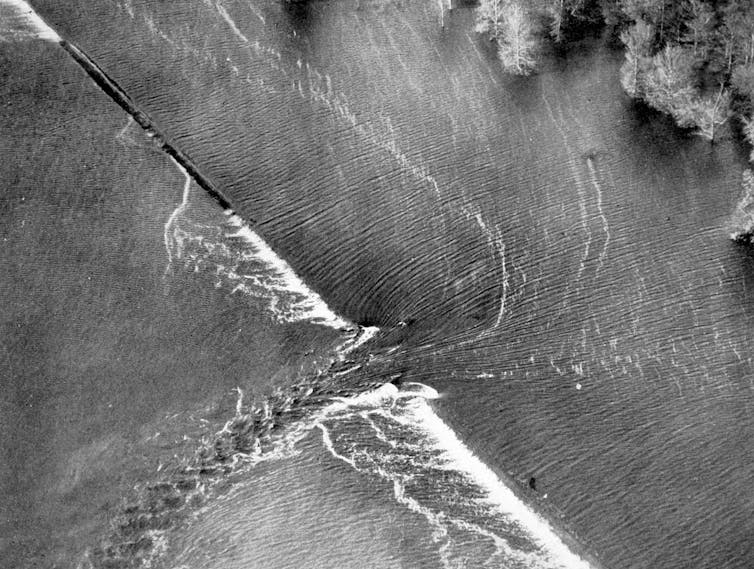
The most typical motive levees fail is overtopping, when water from a river, stream or lake behind the levee flows excessive. As soon as that occurs, erosion can start on the landward facet, weakening the construction from behind. What begins as a gradual trickle can shortly develop right into a breach, creating a big hole within the levee the place water can pour in.
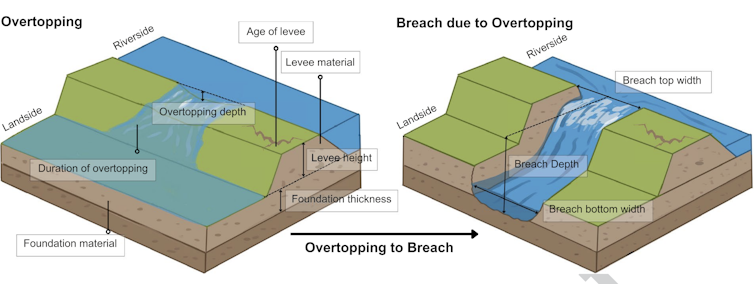
S. Flynn et al., 2025
Atmospheric river storms make the chance of overtopping and breaches a lot increased. These storms ship enormous amounts of rainfall throughout broad areas in a matter of hours, typically mixed with snowmelt. Rivers rise quicker and keep excessive longer. Many levees had been by no means designed for that sort of sustained strain.
When a levee breaches, flooding will be rapid and deep, leaving little time for evacuation and inflicting harm that spreads far past the floodplain.
Who depends on levees right now?
Hundreds of thousands of Individuals dwell and work in space protected by levees, typically with out realizing it. Properties, colleges, highways, rail corridors, ports and energy amenities depend upon the integrity of those constructions.
A recent national study discovered that throughout the contiguous U.S., city enlargement into floodplains occurred greater than twice as quick after levee building because it did in surrounding counties, highlighting how levees can have an effect on communities’ notion of hazard.
Actually, when levees fail, flooding will be worse than in areas with out levees, as a result of water rushes in shortly and drains slowly.
The risks are also uneven, formed by historical past, economics and coverage selections.
That actuality grew to become painfully clear throughout an atmospheric river storm in March 2023 when a levee alongside California’s Pajaro River failed, flooding the town of Pajaro. Pajaro is dwelling to many low-income farmworkers. Floodwaters pressured a whole bunch of residents to evacuate, and a few individuals had been trapped as water ranges rose.
What made the catastrophe particularly troubling was what emerged afterward. Officers and engineers had identified for many years that the Pajaro River levee was weak. Studies documented its weaknesses, however repairs were repeatedly delayed.
Interviews by The Los Angeles Instances and public data confirmed that part of the reason was financial. Choice-makers didn’t prioritize investing in a levee system defending the low-income neighborhood. The chance was identified, however the safety was deferred.
Pajaro isn’t an remoted case. Throughout the nation, disadvantaged communities and communities of color usually tend to depend on older levees or levees that aren’t a part of main federal applications. Rural cities typically depend upon agricultural levees. City neighborhoods could depend on constructions constructed for a a lot smaller inhabitants.
When levees fail, the impacts cascade, closing roads, knocking out energy, contaminating water provides and disrupting lives for years.
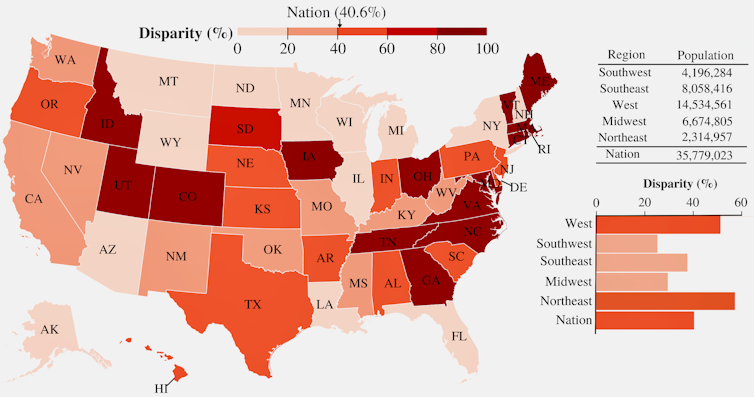
F. Vahedifard et al., 2023
Why this second issues
Advances in engineering, monitoring and danger evaluation have improved how levees are evaluated and designed.
Hurricane Katrina marked a turning level in 2005 when its storm surge broke by levees defending New Orleans. Tons of of individuals died in the flooding. The catastrophe uncovered the implications of neglect and fragmented responsibility for levee repairs.
On the identical time, there was actual progress. Over the previous 20 years, important federal investments have strengthened the condition and management of many of the nation’s levees, notably by the work of federal companies such because the U.S. Military Corps of Engineers.
Nonetheless, the legacy of choices made many years in the past stays, and local weather change is elevating the dangers. Heavier rainfall, quick snowmelt and rising seas are pushing water management programs beyond what many levees were designed to handle. Occasions as soon as thought-about uncommon have gotten extra frequent.
As atmospheric rivers take a look at levees within the West and flood risks grow nationwide, the problem is now not simply technical. It’s about how society values safety, communicates danger and decides whose safety is prioritized.
Levees will proceed to play a significant position in defending communities. Understanding their historical past, and their limits, is important because the storms of the longer term arrive.

