On Jan. 11, 2026, I watched anxiously on the tightly managed Vandenberg Space Force Base in California as an awe-inspiring SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carried NASA’s new exoplanet telescope, Pandora, into orbit.
Exoplanets are worlds that orbit different stars. They’re very tough to watch as a result of – seen from Earth – they seem as extraordinarily faint dots proper subsequent to their host stars, that are tens of millions to billions of occasions brighter and drown out the sunshine mirrored by the planets. The Pandora telescope will be a part of and complement NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in finding out these faraway planets and the celebs they orbit.
I am an astronomy professor at the University of Arizona who makes a speciality of research of planets round different stars and astrobiology. I’m a co-investigator of Pandora and main its exoplanet science working group. We constructed Pandora to shatter a barrier – to know and take away a supply of noise within the information – that limits our means to check small exoplanets intimately and seek for life on them.
Observing exoplanets
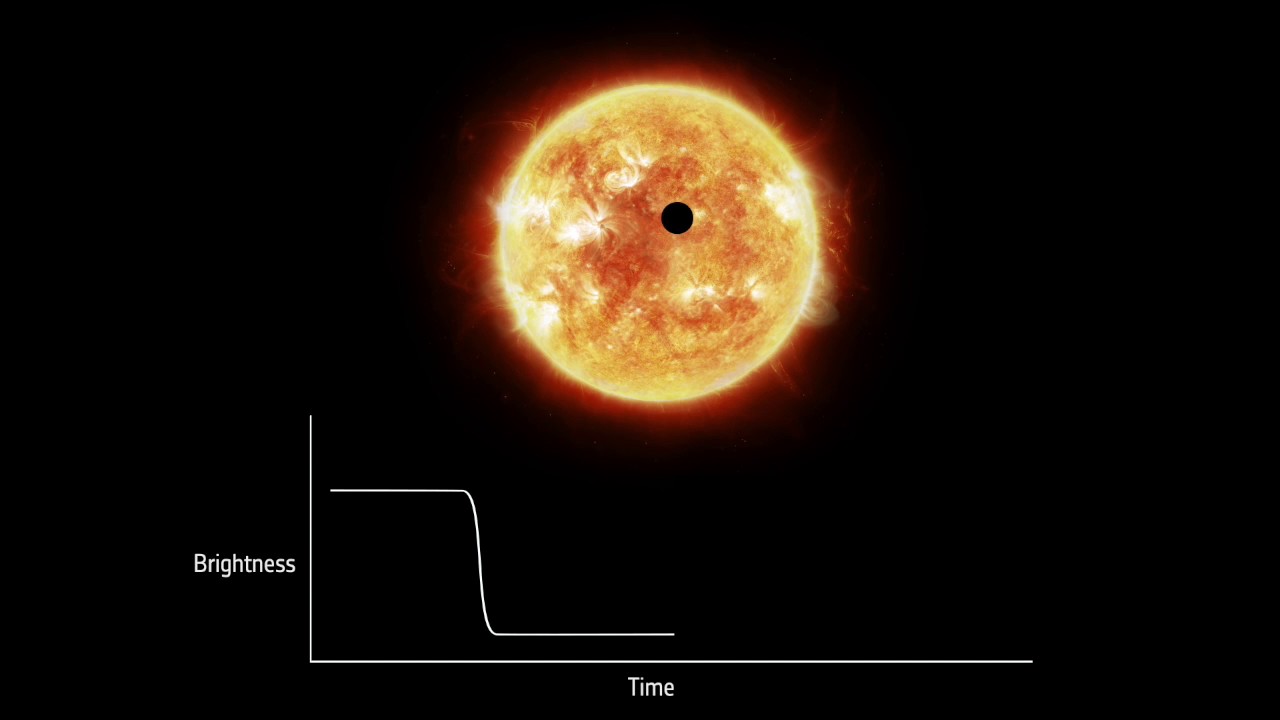
Astronomers have a trick to check exoplanet atmospheres. By observing the planets as they orbit in entrance of their host stars, we will study starlight that filters by their atmospheres.
These planetary transit observations are just like holding a glass of purple wine as much as a candle: The sunshine filtering by will present effective particulars that reveal the standard of the wine. By analyzing starlight filtered by the planets’ atmospheres, astronomers can discover proof for water vapor, hydrogen, clouds and even search for evidence of life. Researchers improved transit observations in 2002, opening an thrilling window to new worlds.
For some time, it appeared to work completely. However, ranging from 2007, astronomers noted that starspots – cooler, energetic areas on the celebs – could disturb the transit measurements.
In 2018 and 2019, then-Ph.D. pupil Benjamin V. Rackham, astrophysicist Mark Giampapa and I printed a series of studies displaying how darker starspots and brighter, magnetically energetic stellar areas can significantly mislead exoplanets measurements. We dubbed this drawback “the transit gentle supply impact.”
Most stars are spotted, active and change continuously. Ben, Mark and I confirmed that these adjustments alter the indicators from exoplanets. To make issues worse, some stars even have water vapor of their higher layers – typically extra distinguished in starspots than outdoors of them. That and different gases can confuse astronomers, who might imagine that they discovered water vapor within the planet.
In our papers – printed three years earlier than the 2021 launch of the James Webb Space Telescope – we predicted that the Webb can’t attain its full potential. We sounded the alarm bell. Astronomers realized that we have been making an attempt to evaluate our wine in gentle of flickering, unstable candles.
Blue Canyon Applied sciences
The delivery of Pandora
For me, Pandora started with an intriguing e mail from NASA in 2018. Two distinguished scientists from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Elisa Quintana and Tom Barclay, requested to talk. They’d an uncommon plan: They wished to construct an area telescope in a short time to assist deal with stellar contamination – in time to help Webb. This was an thrilling thought, but additionally very difficult. House telescopes are very advanced, and never one thing that you’d usually wish to put collectively in a rush.

NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Conceptual Image Lab, CC BY
Pandora breaks with NASA’s standard mannequin. We proposed and constructed Pandora sooner and at a considerably decrease price than is typical for NASA missions. Our method meant protecting the mission easy and accepting considerably increased dangers.
What makes Pandora particular?
Pandora is smaller and can’t gather as a lot gentle as its larger brother Webb. However Pandora will do what Webb can’t: It is going to be in a position to patiently observe stars to know how their advanced atmospheres change.
By gazing a star for twenty-four hours with seen and infrared cameras, it’s going to measure delicate adjustments within the star’s brightness and colours. When energetic areas within the star rotate out and in of view, and starspots kind, evolve and dissipate, Pandora will file them. Whereas Webb very not often returns to the identical planet in the identical instrument configuration and nearly by no means screens their host stars, Pandora will revisit its goal stars 10 occasions over a yr, spending over 200 hours on every of them.
With that info, our Pandora workforce will be capable to determine how the adjustments within the stars have an effect on the noticed planetary transits. Like Webb, Pandora will observe the planetary transit occasions, too. By combining information from Pandora and Webb, our workforce will be capable to perceive what exoplanet atmospheres are manufactured from in additional element than ever earlier than.
After the profitable launch, Pandora is now circling Earth about each 90 minutes. Pandora’s programs and features are actually being examined completely by Blue Canyon Technologies, Pandora’s main builder.
A few week after launch, management of the spacecraft will transition to the University of Arizona’s Multi-Mission Operation Center in Tucson, Arizona. Then the work of our science groups begins in earnest and we’ll start capturing starlight filtered by the atmospheres of different worlds – and see them with a brand new, regular eye.